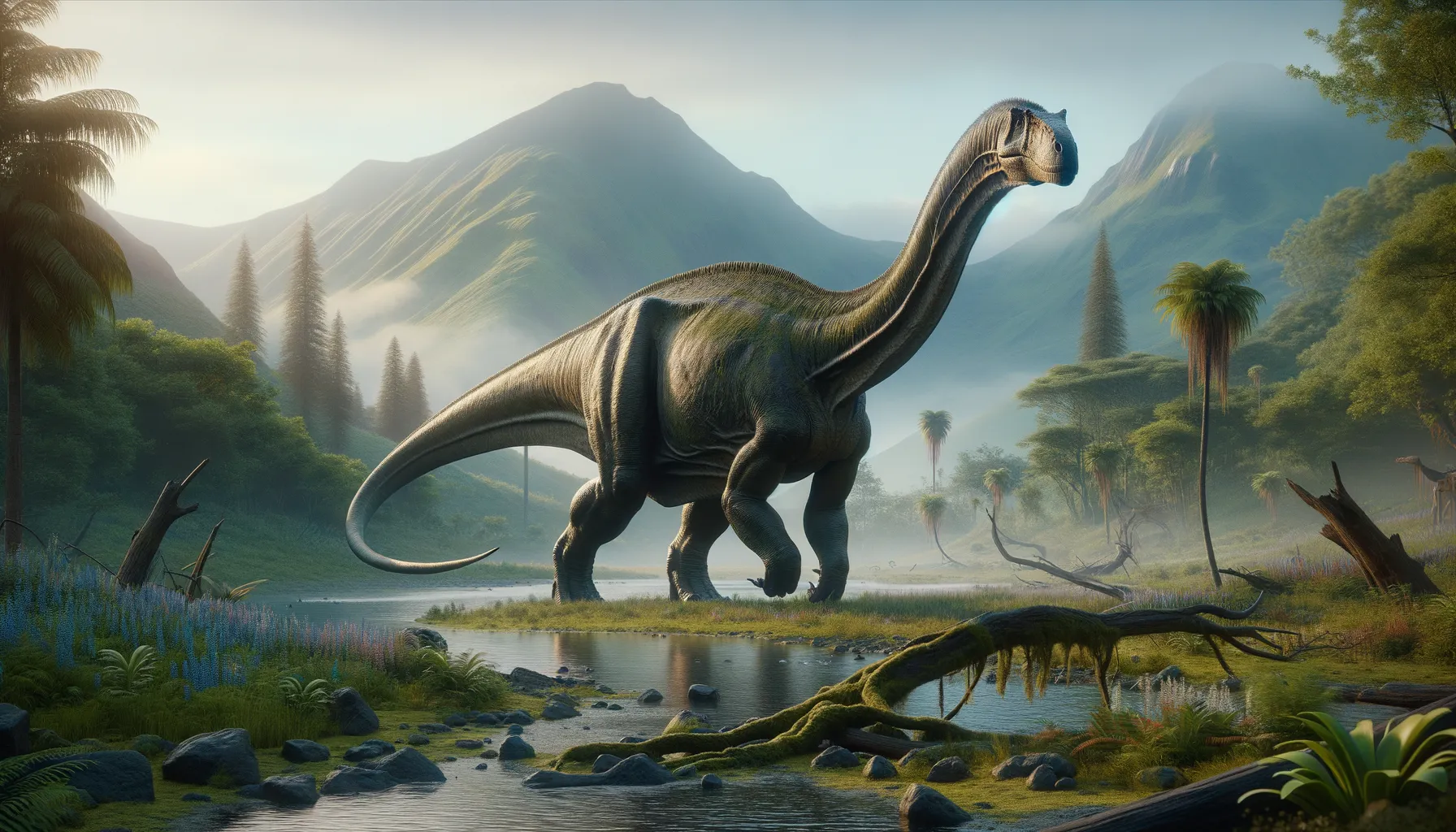
Titanosaurus
A gentle giant from Earth's ancient past.
Period
Cretaceous
Length
Could reach up to 15 to 20 meters in length.
Height
Approximately 9 to 12 meters tall.
Weight
Estimated to weigh around 13 to 25 tons.
Titanosaurus was a gigantic, long-necked plant-eater that roamed the Earth towards the end of the dinosaur era. Known for its massive size, this dinosaur boasts a sturdy body structure and massive legs, which suggest its ability to support great weight. Despite its size, detailed fossil evidence remains somewhat scarce, leading to ongoing debates about its exact classification and characteristics.
Diet
Titanosaurus was an herbivore, primarily consuming vegetation such as leaves, plants, and possibly soft woody material. Its long neck would have allowed it to reach high vegetation or delicate low plants.
Hunting
As a herbivore, Titanosaurus did not actively hunt. It likely spent its days foraging for plant material and using its long neck to reach food in areas that were inaccessible to smaller dinosaurs.
Environmental challenges
Living in the Late Cretaceous period, Titanosaurus faced environmental changes like fluctuating temperatures and diverse ecosystems that required adaptation. Its large size may have made mobility difficult through dense forests and across challenging terrain. Additionally, finding enough food to sustain its massive body might have been a constant challenge, especially as vegetation patterns changed.
Speed
Likely slow-moving due to its massive size.
Lifespan
Estimated to live several decades, akin to large modern reptiles.
First discovery
Fossils were first discovered in India in the late 19th century.
Fun Facts
- Titanosaurus was a massive dinosaur that roamed Earth during the Late Cretaceous period, around 70 million years ago.
- This dinosaur was named 'Titanosaurus' because of its titanic size, with estimates suggesting it could grow up to 40 feet long.
- Despite their enormous size, Titanosaurs were herbivores, meaning they only ate plants.
- Fossils of Titanosaurus have been found on multiple continents, including Asia, South America, and possibly Europe, showing how widespread these giants were.
- Not much is known about Titanosaurus because the fossils often consist of incomplete remains, making this dinosaur somewhat of a mystery.
- Titanosaurus had long necks and tails, which helped them reach high vegetation and balance their massive bodies.
- Its powerful legs supported its huge weight, allowing Titanosaurus to move comfortably through its environment.
Growth and Development
From hatching from eggs, Titanosaurus slowly grew over several years to reach its enormous size. Young Titanosaurus would have been vulnerable to predators until they achieved a size too large and formidable for most threats. Growth rates may have varied due to food availability and environmental conditions.
Habitat
Titanosaurus inhabited a range of environments, from semi-arid plains to lush river valleys. Its presence in different regions suggests adaptability to various climate conditions, from dry areas to potentially more humid environments. Such versatility would have allowed it to exploit a variety of food sources, vital for a creature of its size.
Interaction with other species
Titanosaurus coexisted with a variety of other dinosaur species, including both herbivores and carnivores. Its size likely deterred most predators, though juveniles might have been targeted. It may have competed with other large herbivores for food resources, while offering smaller species protections as they moved in herds.
Natural lifespan
It likely lived several decades, similar to modern large reptiles.
Reproduction
Titanosaurus probably laid eggs, like other sauropods, in nests on the ground. These nests could contain multiple eggs, with juveniles leaving parental care early due to the precocial nature of their development. Little is known about their mating behaviors, but modern reptiles suggest likely seasonal breeding.
Social behaviour
While details are limited, Titanosaurus might have shown some social behavior, possibly moving in groups or herds for protection against predators. It might have communicated through low-frequency calls or physical gestures, similar to behavior seen in elephants today.
Fossil locations
Fossils of Titanosaurus have been found primarily in India, offering key evidence of its presence on the ancient Gondwana landmass. Additional findings, though sparse, suggest they may have inhabited other parts of the southern continents during the Cretaceous period. Its fossil record contributes valuable insights into Late Cretaceous ecosystems.
