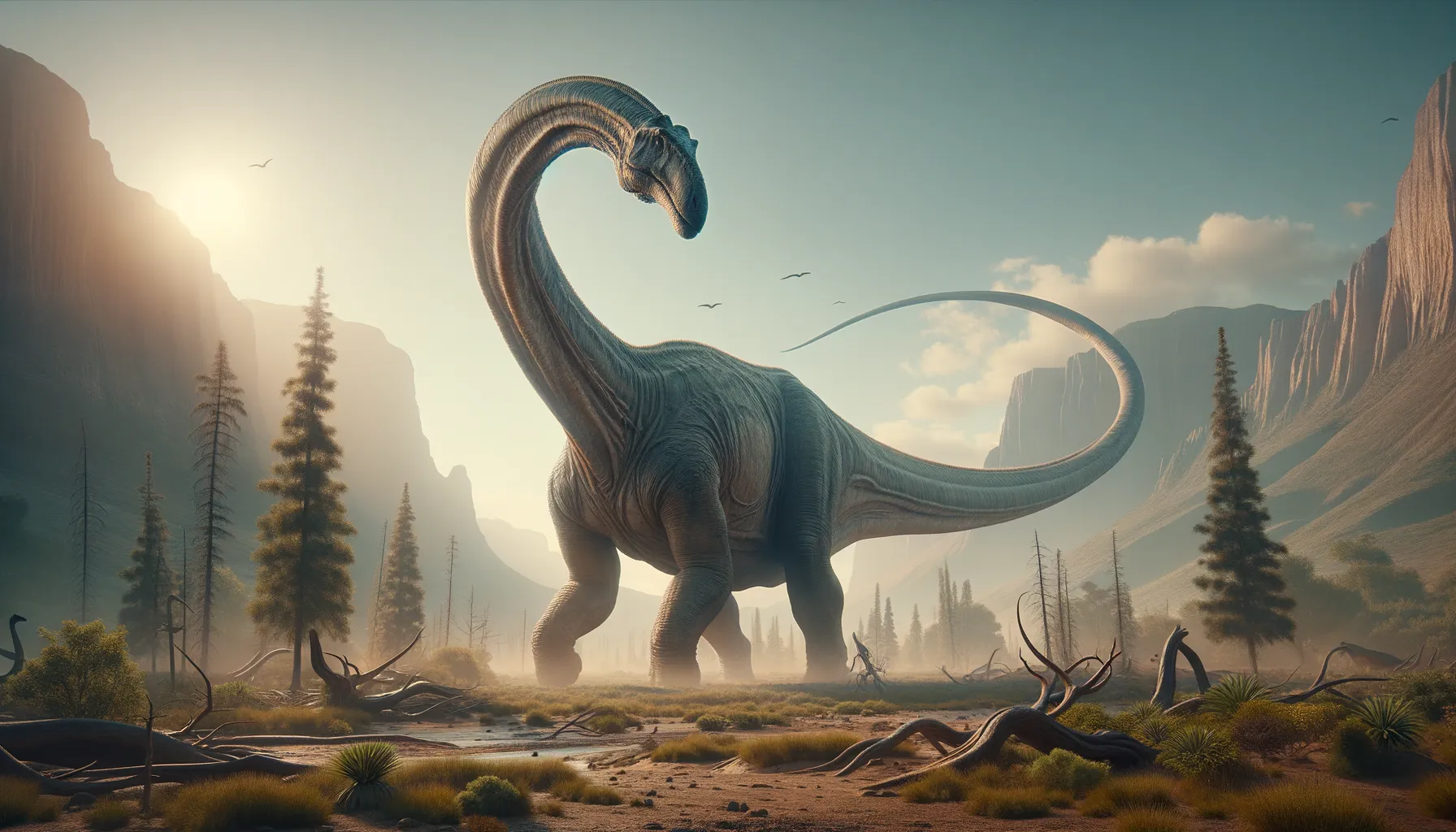
Notocolossus
A colossal giant of the Cretaceous era.
Period
Cretaceous
Length
Could grow up to 85 feet long.
Height
Likely reached up to 30 feet tall.
Weight
Estimated to be around 60 to 80 tons.
Notocolossus was a gigantic sauropod dinosaur that roamed the earth during the Late Cretaceous period. Known for its enormous size, it adds significant insights into dinosaur gigantism. Its discovery in Argentina has provided valuable information on the structure and lifestyle of giant dinosaurs. Notocolossus is part of the family of titanosaurs, characterized by long necks and tails, which were crucial for their survival in their environment.
Diet
Notocolossus was a herbivore, feeding primarily on vegetation such as leaves, plants, and possibly conifers. Due to its large size and long neck, it could reach high branches, accessing food unavailable to smaller dinosaurs.
Hunting
As a herbivore, Notocolossus did not hunt. Instead, it spent much of its time foraging for plants. Its long neck allowed it to graze over wide areas without much movement.
Environmental challenges
Notocolossus faced competition for resources from other large herbivores in its ecosystem. Climate changes and fluctuations in flora availability might have also posed challenges. Predatory dinosaurs would have threatened younger or weaker individuals, necessitating protective measures within herds.
Speed
Slow-moving due to its massive size.
Lifespan
Likely lived for several decades.
First discovery
Discovered in Argentina in 2016.
Fun Facts
- Notocolossus was a gigantic dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period, around 86 million years ago.
- Its fossils were discovered in Argentina, a place known for finding many large dinosaur species.
- Notocolossus is believed to have been one of the largest dinosaurs ever, with estimates suggesting it could have been over 85 feet long.
- The giant size of Notocolossus made it a herbivore, meaning it spent much of its time eating plants.
- One of the most interesting features of Notocolossus is its massive hind limbs, which were key to supporting its enormous weight.
- Despite its size, scientists think Notocolossus might have been able to move somewhat quickly when necessary.
- The name Notocolossus means 'southern giant,' reflecting both its size and the location where it was found.
Growth and Development
Notocolossus likely experienced rapid growth during its early years to achieve such massive size. This growth would have required substantial energy intake and efficient nutrient processing. It is probable that it continued to grow throughout its life, albeit at a slower rate once fully matured.
Habitat
Notocolossus inhabited rich floodplain environments with abundant plant life. These areas provided the necessary resources for feeding its large body. Seasonal changes might have influenced its migrating patterns in search of food and water.
Interaction with other species
Notocolossus coexisted with other dinos, including smaller herbivores and large predators. It may have lived in herds to protect itself from predators. It interacted with the ecosystem by helping to shape vegetation patterns through its feeding habits.
Natural lifespan
Notocolossus likely had a natural lifespan of up to 70 years.
Reproduction
Notocolossus, like other sauropods, may have laid clutches of eggs. These would have been buried in nests made from vegetation or in sandy areas. The survival rate of newborns was likely low, with many falling prey to predators despite protective herding behaviour.
Social behaviour
Notocolossus might have lived in groups to gain protection and enhance foraging efficiency. Such social structures provided safety in numbers, especially for young individuals against predators. Herd dynamics also facilitated learning and communication among individuals.
Fossil locations
Fossil remains of Notocolossus were found in Mendoza Province, Argentina. These discoveries have allowed paleontologists to better understand the diversity and distribution of titanosaurs. The fossils include a partial skeleton, offering essential details about its structure and lifestyle.
